Your Choice for Medical, Private and Senior Rides
Driven By Care
Guided By Trust
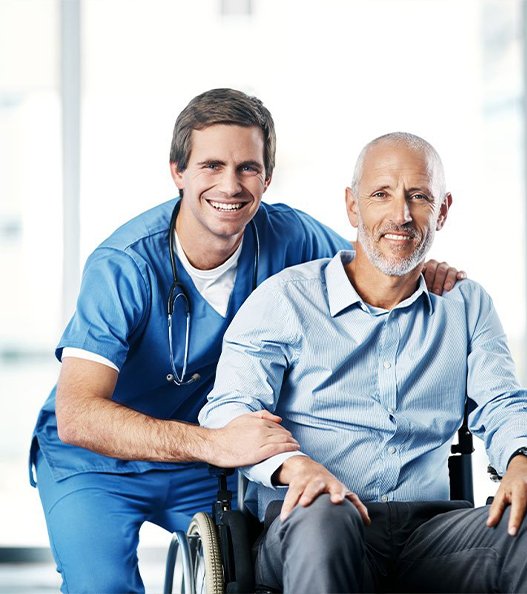

Our Mission
Exceptional service. Reliable rides. Groovy every time.
Groovy Transportation
Reliable & Compassionate Non-Medical Transport
At Groovy Transportation, we understand that medical, social, and psychological health is really important. We are based in the heart of Missouri and specialize in providing various non-emergency medical transportation services. We serve Columbia, St. Louis, Lebanon, and surrounding areas, ensuring each ride is comfortable, safe, and timely. Ensuring each ride is comfortable, safe, and punctual.
We ensure seamless Transportation for our patients. Our vehicles are equipped with patient requirements like Ambulances, long-distance Transportation, senior Transportation, wheelchairs, ramps, lifts, and equipment to assist patients with limited mobility.
Groovy Transportation Smart, Reliable Travel
Groovy Transportation offers dependable, stylish rides with professional drivers and hassle-free booking. Whether it’s daily travel or special events, we make every journey smooth, safe, and enjoyable.
Expertise and Compassion
Trust our experienced, compassionate drivers to make your journey smooth, whether you’re in Missouri (Columbia, St. Louis, or Lebanon).

Modern Comfort
Experience ease with our state-of-the-art, well-maintained designed vehicles, our state-of-the-art, designed for optimal comfort and accessibility.

Tailored to You
Enjoy personalized services crafted to meet your unique non-emergency medical needs, prioritizing your non-emergency medical satisfaction.

Punctuality Promise
Reliability in every ride – we’re dedicated to punctuality, ensuringensuring you reach your destination on time, every time.

Customer-Centric
Your feedback fuels our growth – we embrace a customer-centric approach, continually enhancing our services for your satisfact

Patient Comfort
More than just a ride—it's our commitment. With top-tier vehicles and trained drivers, we prioritize your comfort in every journey.
Choose Us For Smoot Transporation
Groovy Transportation Trip Request
Groovy Transportation – Driving comfort, safety, and care every mile of the way.
Our Promise Transportation When You Need It
We provide safe, on-time rides for NEMT patients going to medical appointments, therapy, or treatments—always with care and respect.
Ambulatory Transportation
Groovy Transportation offers ambulatory services for those who need safe, comfortable rides to medical appointments or prefer a reliable alternative to taxis, without the need for a wheelchair or stretcher.
Wheelchair Transportation
Empower your journey with Groovy Transportation’s wheelchair services across Missouri. Offering safe, timely rides to medical appointments, social events, and errands with advanced vehicles, ramps, and secure tie-downs.
Dialysis
Transportation
Groovy Transportation offers reliable, on-time dialysis rides in Columbia, St. Louis, and Lebanon. Enjoy comfortable, affordable NEMT services, ensuring safe transport for your dialysis appointments in Missouri. Book now!
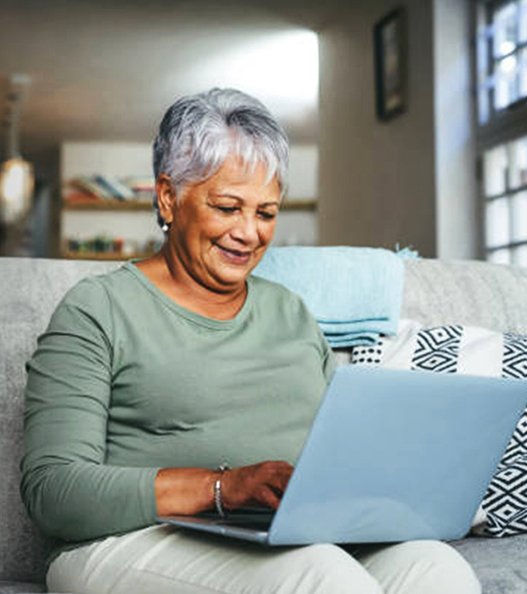
Senior Transportation Service
Senior Citizen Transportation in Missouri helps seniors with safe, reliable rides to appointments, social events, shopping, and more. Our trained drivers ensure comfort with wheelchair-accessible vehicles and secure transport.
Long Distance Transportation
Groovy Transportation offers safe, comfortable long-distance transport across Missouri, including Columbia, St. Louis, and Lebanon. We prioritize safety, skilled drivers, and tailored solutions for medical, business, and personal travel.
Medical
Transportation
Groovy Transportation offers safe, comfortable medical transport across Missouri, including Columbia, St. Louis, and Lebanon. We prioritize safety, trained drivers, and reliable service for check-ups, hospital visits, and long-distance care.
Book your ride today for a safe and smooth journey!
Book Your Ride Today For a Stress-Free Journey!

How to Book Groovy Transportation?
-
Call Us at (571) 474-7100
Speak with our friendly customer service representatives to schedule a ride. They’ll guide you through the process and answer any questions you have. -
Use Our Online Booking Form
For added convenience, you can also book your ride directly from our website. Just fill out our simple booking form, and we’ll take care of the rest! -
Set Up Recurring Rides
If you have regular medical appointments, we can arrange recurring rides, ensuring you have reliable transportation whenever you need it. Just let us know your schedule, and we’ll be there!
Clarifying Concerns, Enhancing Confidence: Your Questions Answered
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Book with Groovy?
Booking a ride is easy! Simply contact us at (571) 474-7100) or use our online booking form on the website. We’ll be happy to assist you.
What areas do you serve?
We proudly serve the Missouri area, Columbia, Jefferson City, Randolph County, Moniteau County, Howard County, Cooper County, Cole County, Callaway County, Boone County, Audrain County, Mexico, Boonville, Fayette, Tipton and Moberly providing reliable and comfortable non-emergency medical transportation to our community.
Are your vehicles wheelchair accessible?
Yes, our fleet includes state-of-the-art vehicles that are wheelchair accessible, ensuring a comfortable ride for all our passengers.
How can I be sure your services are punctual?
At Groovy Transportation, we prioritize punctuality. Our drivers are well-versed with the routes in Missouri and utilize real-time traffic updates to ensure timely arrivals.
Is Groovy Transportation insured and licensed?
Yes, we are a fully licensed and insured non-emergency medical transportation provider, committed to upholding the highest standards of safety and reliability.
How are your drivers trained?
Our drivers undergo rigorous training in defensive driving, patient care, and customer service. They are dedicated to providing a safe and compassionate transportation experience.
CITIES WE SERVE
We proudly serve Columbia, Ashland, Hallsville, and Centralia, along with surrounding areas in Missouri. At Groovy, we provide safe, reliable, and timely non-emergency medical transportation. From ambulatory and wheelchair services to senior rides and long-distance travel, our team ensures every trip is comfortable and stress-free. Wherever you are nearby, Groovy is here to get you where you need to go with care.
Testimonials
What Our Clients Says About Us
Our clients consistently praise Groovy Transportation for our punctuality, professionalism, and exceptional service. Whether it’s a quick airport transfer or a special event ride, they love the comfort, cleanliness, and style of our vehicles. Many highlight our friendly drivers and smooth booking process, saying it makes every trip stress-free and enjoyable. Their glowing reviews motivate us to keep raising the bar every day.
Groovy Transportation made my airport transfer stress-free. The driver was early, the car was spotless, and the whole experience was smooth. I’ll definitely be booking again!

Kevin Andrew
Happy CustomerGroovy Transportation is Professional, punctual, and polite! Groovy exceeded my expectations. From booking to drop-off, everything was seamless. I felt safe and comfortable the entire ride.

Alina Parker
Happy CustomerGroovy Transportation truly cares. Every ride we've taken has been safe, on time, and comfortable. Their wheelchair-accessible vehicles and friendly drivers make a real difference.

Jessica
Happy CustomerBusiness Address:
3705 Lyman Dr Columbia, MO 65203, USA
Phone Number:
Operating Hours:
Mon – Sat: 4 am – 8pm
Sunday: 7 am – 5 pm


